posterior labral tear shoulder mri
To provide the highest quality clinical and technology services to customers and patients, in the spirit of continuous improvement and innovation. He or she may perform specific tests by placing your arm in different positions to reproduce your symptoms. The results of these tests will help your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is necessary. Alterations in function of the serratus anterior muscle may disrupt the scapulothoracic rhythm leading to loss of power and stability of the glenoid and variable amounts of scapular winging.6. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Notice the abnormal contour of the anterior glenoid and the avulsed anterior rim (arrow). Surg Clin North Am. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthrographic findings with arthroscopic correlation. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. (Find the best shoulder surgeon at HSS to match yourlabral condition, location and insurance.). Posterior dislocation-fracture. Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. in Radiology in 2008 examined 36 patients following acute traumatic shoulder dislocation and revealed full-thickness tears in 19% of patients and partial or full-thickness tears in 42%.17As would be expected, subscapularis tears were most common, but tears were also identified in the supraspinatus and the infraspinatus. posterior shoulder dislocation Radiographic features MRI On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. How long you require a sling depends upon the severity of your injury. Fluid undermines a tear of the posterior glenoid labrum (arrow) in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder pain. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. Superior labral anterior posterior tear. On the transscapular-Y view the humeral head is displaced posteriorly. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthroscopic findings with arthroscopic correlation. Snyder et al. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Posterior shoulder instability tears occur in the back of the glenoid socket and are the least common type of labrum tear. The chondral lesion is thought to arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head. The major restraints to posterior instability include the posterior capsule and glenohumeral ligaments, the rotator interval, the labrum, the glenoid, and the musculature of the rotator cuff and shoulder. October 2000 RadioGraphics, 20, S67-S81. The negative impact that posterior labral injuries have on a combine participants early NFL performance is important to consider especially because of how often these injuries occur among elite football players. 37-year-old man with shoulder injury and posterior labral tear. During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts the arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder joint. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis, Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound, Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions, Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013, Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System, Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels, Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels, Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation, Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions, TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System, How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions, Usefulness of the Abduction and External Rotation Views in Shoulder MR Arthrography, MR Imaging and MR Arthrography of Paraglenoid Labral Cysts, CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. If the injury is a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, the physician (or even a team coach or patient themselves) can usually pop the shoulder back into place a process called reduction and then follow up with physical therapy to strengthen the muscles. 2003;181(6):1449-62. Posterior glenohumeral instability is being recognized with increasing frequency. A Bankart tear can extend to the 1-3 o'clock position, but then there should also be a tear in the 3-6 o'clock position. The epidemiology and biomechanics of throwing injuries are reviewed, and examples from the authors institutional experience with competitive, collegiate, and professional baseball players are provided to demonstrate the constellation of unique imaging findings seen in overhead throwing athletes. The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. 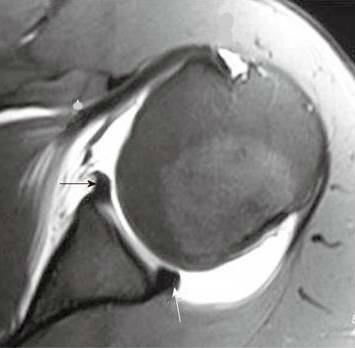 Keith W. Harper1, Clyde A. Helms1, Clare M. Haystead1 and Lawrence D. Higgins Glenoid Dysplasia: Incidence and Association with Posterior Labral Tears as Evaluated on MRI. Skeletal Radiol. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. (2013) ISBN: 9780323081771 -. Clavert P. Glenoid Labrum Pathology. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview Injuries isolated to labrum and capsule can often be successfully repaired with arthroscopic techniques including capsulolabral repair, capsular shift, and capsular shrinkage.
Keith W. Harper1, Clyde A. Helms1, Clare M. Haystead1 and Lawrence D. Higgins Glenoid Dysplasia: Incidence and Association with Posterior Labral Tears as Evaluated on MRI. Skeletal Radiol. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. (2013) ISBN: 9780323081771 -. Clavert P. Glenoid Labrum Pathology. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview Injuries isolated to labrum and capsule can often be successfully repaired with arthroscopic techniques including capsulolabral repair, capsular shift, and capsular shrinkage.  May, David G. Disler. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Non-surgical treatment tends to be most successful in patients with a history of atraumatic subluxations, whereas patients who experience an acute, traumatic posterior dislocation are much less likely to report successful outcomes from conservative therapy.19 Non-operative therapy focuses on strengthening the dynamic shoulder stabilizers and activity modification. Persistent pain is not typical and may point to additional pathology of the rotator cuff or biceps tendon6. Shah N and Tung GA. Tears to the specialized cartilage tissue in the shoulder known as the labrum can cause pain and instability in the shoulder. The shoulder, because of its wide range of motion, is anatomically predisposed to instability, but the vast majority of shoulder instability is anterior, with posterior instability estimated to affect 2-10% of unstable shoulders.1Although anterior shoulder dislocations have been recognized since the dawn of medicine, the first medical description of posterior shoulder dislocation did not occur until 1822.2In modern times, posterior shoulder instability is still a commonly missed diagnosis, in part due to a decreased index of suspicion for the entity among many physicians. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Snyder et al. Consecutive fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial images at the mid glenoid in a football player with persistent shoulder pain reveals mild glenoid dysplasia, with a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid rim (arrows). Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 12) or at the humeral attachment (Fig. 7-9). On CT it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment of the anterior glenoid (arrow). The SLAP tear can continue posteriorly and can contribute to posterior shoulder pain. 4. However, a study by Saupe et al. Philip Robinson. WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. xZ[oF~GxiWEi$zI)3PD97e./o]7,?8bqi&VP>}e Figure 2. SLAP is an acronym that stands for 'Superior Labral tear from Anterior to Posterior'. On the transscapular-Y view the humeral head is displaced posteriorly. The approach to surgery is dependent upon the type of injuries sustained by the patient, and the developmental or acquired alterations in anatomy that may be present. Contusion and edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction (arrowhead). It is seen in 75-100% of patients with anterior instability. Numerous labral abnormalities may be encountered in patients with posterior glenohumeral instability. Imaging signs of posterior glenohumeral instability. Evaluation and management of posterior shoulder instability. Rotator cuff tears in the context of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to be rare. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993 : 85-96. Bankart lesions with an osseus fragment are common findings in patients with an anterior dislocation and are frequently seen on the x-rays or CT-scan. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). SLAP tears are usually treated with rest, anti-inflammatory medications and, in some cases, an in-office cortisone injection. 4). %
Glenoid labral tear. 1 0 obj
It is not clear whether the labrum is normal. An ALPSA-lesion is an Anterior Labral Periosteal Sleeve Avulsion. Another patient with an avulsion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament from the humeral insertion. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. Figure 1. A Bankart lesion is an injury of the anterior glenoid labrum due to anterior shoulder dislocation. In cases of severe dysplasia, advanced rounding and posterior sloping of the posterior glenoid is seen, and pronounced thickening of the labrum and other adjacent posterior soft tissues is apparent. Musculoskeletal MRI. Those undergoing open surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and in some cases incomplete shoulder rotation. There is an osseus Bankart lesion (curved red arrow). . On the AP-view the head looks strange due to the internal rotation. To make a tear in the labrum show up more clearly on the MRI, a dye may be injected into your shoulder before the scan is taken. Normal glenoid morphology is present. The biceps tendon is medially dislocated (short arrow). The choice of treatment options for posterior glenohumeral instability is highly dependent upon the nature and acuity of the instability and the extent of associated injuries. WebThe labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 This is a bone defect as result of the impaction of the glenoid rim on the humeral head. Bankart lesions are typically located in the 3-6 o'clock position because that's where the humeral head dislocates. Mr Watson will decide the best repair option based upon the type of tear you have, as well as your age, activity level, and the presence of any other injuries seen during the surgery. In atraumatic posterior instability there is no history of major trauma, however, there is almost always an element of repetitive microtrauma causing labral pathology and posterior capsular stretching. Patients with periosteal sleeve avulsions, such as the POLPSA, are more likely to be symptomatic.9. This top area is also where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. The humeral head is almost always displaced anteriorly and medially below the coracoid process. This means that MR-arthrography with the arm in the neutral position may fail to detect the labral tear. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Ferrari JD, Ferrari DA, Coumas J, Pappas AM. De Maeseneer M, Van Roy F, Lenchik L et al. This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). Scroll through the images. 2015;6(9):660-71. Flexibility and range-of-motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder capsule, which is the strong connective tissue that surrounds the joint. The subscapularis muscle has been identified as the most important muscle in resisting posterior subluxation of the humerus.5 Asynchrony of scapulothoracic and glenohumeral muscle contraction may compromise the stability of the glenohumeral joint. Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. A tear undercuts the posterior labrum (small arrow). <>>>
AJR 1998; 171:763-768. CT arthrography has been reported to have 97.3% accuracy for detecting Bankart lesions and 86.3% for SLAP lesions 4, which makes it comparable with MR arthrography and gives the possibility to examine the patients with contraindications to an MR examination. The labrum deepens the socket of the shoulder joint, making it a stronger fit for the head of the humerus. MRI is not uncommonly the key to the diagnosis as patients may present with vague clinical findings that are not prospectively diagnosed, in part because of the relatively less common incidence and awareness of this entity. Regardless of which type of surgery is performed, almost all athletes are advised to wear a sling for the first four weeks after surgery to protect the shoulder as it heals. Such lesions are generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability. Posterior dislocations are uncommon and not as obvious on the X-rays as an anterior dislocation. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear 2016). The epidemiology and biomechanics of throwing injuries are reviewed, and examples from the authors institutional experience with competitive, collegiate, and professional baseball players are provided to demonstrate the constellation of unique imaging findings seen in overhead throwing athletes. Webshoulder. MRA( ) . The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. 2004;12(1):97-109, vi-vii. In the ABER position however there is tension on the antero-inferior labrum by the stretched anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament and you have more chance to detect the tear. Posterior subluxation of the humeral head is also apparent. The shoulder almost always dislocates to anterior and inferior, because motion to superior is limited by the acromion, coracoid process and rotator cuff (figure). 11). This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. The arrow points to the disrupted periosteum. Repair options. Arthroscopy. Next notice the high signal at 12 o' clock (red arrows). The coronal images shows the medially displaced labrum (red arrow). 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. (2b) The T2-weighted sagittal image confirms posterior displacement of the humeral head (arrow) relative to the glenoid (asterisk). A displaced tear of the posteroinferior labrum is present, with a torn piece of periosteum (arrow) remaining attached to the posterior labrum. J Am Med Assoc 117: 510-514, 1941. The images show a subtle Bankart fracture (arrows). The images show a partial tear of the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage at the 4-6 o 'clock position (arrows). The posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). The arrow points to the medially displaced labroligamentous complex. Glenoid labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid labrum and a possible cause of shoulder pain. 2008 Aug; 24(8):921-9. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. In some cases, the labrum can heal with rest and physical therapy, depending on the severity of the tear. 15,16). Notice the medially displaced labrum. AJR 2003;180:369-75. endobj
On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Essential Radiology for Sports Medicine. 3. Direct trauma to the anterior shoulder, a posteriorly directed force on an adducted arm (fall on outstretched hand), and indirect muscle forces (seizure and electrical shock) are typical etiologies. Saupe N, White LM, Bleakney R, et al. What is your diagnosis? Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. The anterior labrum is absent at the 1-3 o 'clock position There are several different types of SLAP tears. The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. 2002 Jul;31(7):396-9. A GLAD-lesion is a GlenoLabral Articular Disruption. The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Jabaz D, Knipe H, et al. (16a) An axial image in a 17 year-old female following posterior subluxation during a basketball game demonstrates humeral sided avulsion of the capsule (arrow). (7a) A coronal T2-weighted fat-suppressed image through the posterior glenohumeral joint in a patient following posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates hemorrhage and edema at the interrupted humeral insertion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament compatible with a posterior band inferior glenohumeral ligament avulsion (PHAGL). There is a superior dislocation of the humeral head. Figure 1. In many cases, the initial treatment for a SLAP injury is nonsurgical. The labrum acts both as a bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the shoulder. (4a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a severely retroverted glenoid (arrowheads) and posterior glenoid hypoplasia with a hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrow). 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear Following a posterior subluxation event, a fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image in this 52 year-old male reveals focal edema and irregularity at the humeral attachment of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (arrow), compatible with a partial tear. It represents a patial tear of the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage. To provide the highest quality clinical and technology services to customers and patients, in the spirit of continuous improvement and innovation. SLAP tears involve the superior glenoid labrum, where the long head of biceps tendon inserts. Adapted with permission fromhttps://orthoinfo.aaos.org. (2a) The posterior labrum (arrow) is torn from the posterior glenoid and displaced posteriorly. Motion in a posterior direction is limited by the posterior rim of the glenoid which is in an anteverted position. 1 Hawkins RJ, Koppert G, Johnston G. Recurrent posterior instability (subluxation) of the shoulder. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult- Online and Print),4. As joint instability is often present, capsuloplasty may be added to the procedure. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. The negative impact that posterior labral injuries have on a combine participants early NFL performance is important to consider especially because of how often these injuries occur among elite football players. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. The dislocation of the humeral head to antero-inferior causes damage to the antero-inferior rim of the glenoid in the 3 - 6 o'clock position (marked in red). The posterior labrum is enlarged to replace the deficient glenoid rim. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. The findings are compatible with a posterior GLAD lesion (glenolabral articular disruption). . 11 ). The ABER-view shows an absent antero-inferior labrum. Comparison with the contralateral shoulder is critical in identifying significant shoulder subluxation versus normal laxity. "If fixed properly, most athletes should be able to return to at least 80 percent of their pre-injury level of play," says Dr. Fealy. Clinical History: A 37 year-old male presents with shoulder discomfort, particularly in adduction and mild internal rotation. Lesions of the labrum, rotator cuff musculature, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior glenohumeral subluxation. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. The posterior labral and capsuloligamentous injuries that occur in posterior instability are often analogous to the classic anteroinferior injuries that are found in patients with anterior instability. 9 Tung GA, Hou DD. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). This is a post-reduction view. Arthroscopy. This in turn creates instability because the breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder to dislocate again. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. 2012;132(7):905-19. The majority of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a SLAP tear. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. This is a difficult case. Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum, and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. The normal orientation of the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by the dotted line. Bennett GE: Shoulder and elbow lesions of the professional baseball pitcher. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Due to these recurrent dislocations significant bone loss and erosion of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, which maintains the unstable situation. Your doctor will test your range of motion by having you move your arm in different directions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. When the shoulder joint ball slips out of the socket, the joint capsule (fiberous tissues that surround and protect the joint) can pull on the lower portion of the labrum and tear it. %PDF-1.5
A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk).
May, David G. Disler. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Non-surgical treatment tends to be most successful in patients with a history of atraumatic subluxations, whereas patients who experience an acute, traumatic posterior dislocation are much less likely to report successful outcomes from conservative therapy.19 Non-operative therapy focuses on strengthening the dynamic shoulder stabilizers and activity modification. Persistent pain is not typical and may point to additional pathology of the rotator cuff or biceps tendon6. Shah N and Tung GA. Tears to the specialized cartilage tissue in the shoulder known as the labrum can cause pain and instability in the shoulder. The shoulder, because of its wide range of motion, is anatomically predisposed to instability, but the vast majority of shoulder instability is anterior, with posterior instability estimated to affect 2-10% of unstable shoulders.1Although anterior shoulder dislocations have been recognized since the dawn of medicine, the first medical description of posterior shoulder dislocation did not occur until 1822.2In modern times, posterior shoulder instability is still a commonly missed diagnosis, in part due to a decreased index of suspicion for the entity among many physicians. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Snyder et al. Consecutive fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial images at the mid glenoid in a football player with persistent shoulder pain reveals mild glenoid dysplasia, with a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid rim (arrows). Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 12) or at the humeral attachment (Fig. 7-9). On CT it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment of the anterior glenoid (arrow). The SLAP tear can continue posteriorly and can contribute to posterior shoulder pain. 4. However, a study by Saupe et al. Philip Robinson. WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. xZ[oF~GxiWEi$zI)3PD97e./o]7,?8bqi&VP>}e Figure 2. SLAP is an acronym that stands for 'Superior Labral tear from Anterior to Posterior'. On the transscapular-Y view the humeral head is displaced posteriorly. The approach to surgery is dependent upon the type of injuries sustained by the patient, and the developmental or acquired alterations in anatomy that may be present. Contusion and edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction (arrowhead). It is seen in 75-100% of patients with anterior instability. Numerous labral abnormalities may be encountered in patients with posterior glenohumeral instability. Imaging signs of posterior glenohumeral instability. Evaluation and management of posterior shoulder instability. Rotator cuff tears in the context of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to be rare. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993 : 85-96. Bankart lesions with an osseus fragment are common findings in patients with an anterior dislocation and are frequently seen on the x-rays or CT-scan. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). SLAP tears are usually treated with rest, anti-inflammatory medications and, in some cases, an in-office cortisone injection. 4). %
Glenoid labral tear. 1 0 obj
It is not clear whether the labrum is normal. An ALPSA-lesion is an Anterior Labral Periosteal Sleeve Avulsion. Another patient with an avulsion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament from the humeral insertion. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. Figure 1. A Bankart lesion is an injury of the anterior glenoid labrum due to anterior shoulder dislocation. In cases of severe dysplasia, advanced rounding and posterior sloping of the posterior glenoid is seen, and pronounced thickening of the labrum and other adjacent posterior soft tissues is apparent. Musculoskeletal MRI. Those undergoing open surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and in some cases incomplete shoulder rotation. There is an osseus Bankart lesion (curved red arrow). . On the AP-view the head looks strange due to the internal rotation. To make a tear in the labrum show up more clearly on the MRI, a dye may be injected into your shoulder before the scan is taken. Normal glenoid morphology is present. The biceps tendon is medially dislocated (short arrow). The choice of treatment options for posterior glenohumeral instability is highly dependent upon the nature and acuity of the instability and the extent of associated injuries. WebThe labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 This is a bone defect as result of the impaction of the glenoid rim on the humeral head. Bankart lesions are typically located in the 3-6 o'clock position because that's where the humeral head dislocates. Mr Watson will decide the best repair option based upon the type of tear you have, as well as your age, activity level, and the presence of any other injuries seen during the surgery. In atraumatic posterior instability there is no history of major trauma, however, there is almost always an element of repetitive microtrauma causing labral pathology and posterior capsular stretching. Patients with periosteal sleeve avulsions, such as the POLPSA, are more likely to be symptomatic.9. This top area is also where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. The humeral head is almost always displaced anteriorly and medially below the coracoid process. This means that MR-arthrography with the arm in the neutral position may fail to detect the labral tear. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Ferrari JD, Ferrari DA, Coumas J, Pappas AM. De Maeseneer M, Van Roy F, Lenchik L et al. This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). Scroll through the images. 2015;6(9):660-71. Flexibility and range-of-motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder capsule, which is the strong connective tissue that surrounds the joint. The subscapularis muscle has been identified as the most important muscle in resisting posterior subluxation of the humerus.5 Asynchrony of scapulothoracic and glenohumeral muscle contraction may compromise the stability of the glenohumeral joint. Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. A tear undercuts the posterior labrum (small arrow). <>>>
AJR 1998; 171:763-768. CT arthrography has been reported to have 97.3% accuracy for detecting Bankart lesions and 86.3% for SLAP lesions 4, which makes it comparable with MR arthrography and gives the possibility to examine the patients with contraindications to an MR examination. The labrum deepens the socket of the shoulder joint, making it a stronger fit for the head of the humerus. MRI is not uncommonly the key to the diagnosis as patients may present with vague clinical findings that are not prospectively diagnosed, in part because of the relatively less common incidence and awareness of this entity. Regardless of which type of surgery is performed, almost all athletes are advised to wear a sling for the first four weeks after surgery to protect the shoulder as it heals. Such lesions are generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability. Posterior dislocations are uncommon and not as obvious on the X-rays as an anterior dislocation. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear 2016). The epidemiology and biomechanics of throwing injuries are reviewed, and examples from the authors institutional experience with competitive, collegiate, and professional baseball players are provided to demonstrate the constellation of unique imaging findings seen in overhead throwing athletes. Webshoulder. MRA( ) . The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. 2004;12(1):97-109, vi-vii. In the ABER position however there is tension on the antero-inferior labrum by the stretched anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament and you have more chance to detect the tear. Posterior subluxation of the humeral head is also apparent. The shoulder almost always dislocates to anterior and inferior, because motion to superior is limited by the acromion, coracoid process and rotator cuff (figure). 11). This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. The arrow points to the disrupted periosteum. Repair options. Arthroscopy. Next notice the high signal at 12 o' clock (red arrows). The coronal images shows the medially displaced labrum (red arrow). 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. (2b) The T2-weighted sagittal image confirms posterior displacement of the humeral head (arrow) relative to the glenoid (asterisk). A displaced tear of the posteroinferior labrum is present, with a torn piece of periosteum (arrow) remaining attached to the posterior labrum. J Am Med Assoc 117: 510-514, 1941. The images show a subtle Bankart fracture (arrows). The images show a partial tear of the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage at the 4-6 o 'clock position (arrows). The posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). The arrow points to the medially displaced labroligamentous complex. Glenoid labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid labrum and a possible cause of shoulder pain. 2008 Aug; 24(8):921-9. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. In some cases, the labrum can heal with rest and physical therapy, depending on the severity of the tear. 15,16). Notice the medially displaced labrum. AJR 2003;180:369-75. endobj
On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Essential Radiology for Sports Medicine. 3. Direct trauma to the anterior shoulder, a posteriorly directed force on an adducted arm (fall on outstretched hand), and indirect muscle forces (seizure and electrical shock) are typical etiologies. Saupe N, White LM, Bleakney R, et al. What is your diagnosis? Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. The anterior labrum is absent at the 1-3 o 'clock position There are several different types of SLAP tears. The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. 2002 Jul;31(7):396-9. A GLAD-lesion is a GlenoLabral Articular Disruption. The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Jabaz D, Knipe H, et al. (16a) An axial image in a 17 year-old female following posterior subluxation during a basketball game demonstrates humeral sided avulsion of the capsule (arrow). (7a) A coronal T2-weighted fat-suppressed image through the posterior glenohumeral joint in a patient following posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates hemorrhage and edema at the interrupted humeral insertion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament compatible with a posterior band inferior glenohumeral ligament avulsion (PHAGL). There is a superior dislocation of the humeral head. Figure 1. In many cases, the initial treatment for a SLAP injury is nonsurgical. The labrum acts both as a bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the shoulder. (4a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a severely retroverted glenoid (arrowheads) and posterior glenoid hypoplasia with a hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrow). 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear Following a posterior subluxation event, a fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image in this 52 year-old male reveals focal edema and irregularity at the humeral attachment of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (arrow), compatible with a partial tear. It represents a patial tear of the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage. To provide the highest quality clinical and technology services to customers and patients, in the spirit of continuous improvement and innovation. SLAP tears involve the superior glenoid labrum, where the long head of biceps tendon inserts. Adapted with permission fromhttps://orthoinfo.aaos.org. (2a) The posterior labrum (arrow) is torn from the posterior glenoid and displaced posteriorly. Motion in a posterior direction is limited by the posterior rim of the glenoid which is in an anteverted position. 1 Hawkins RJ, Koppert G, Johnston G. Recurrent posterior instability (subluxation) of the shoulder. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult- Online and Print),4. As joint instability is often present, capsuloplasty may be added to the procedure. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. The negative impact that posterior labral injuries have on a combine participants early NFL performance is important to consider especially because of how often these injuries occur among elite football players. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. The dislocation of the humeral head to antero-inferior causes damage to the antero-inferior rim of the glenoid in the 3 - 6 o'clock position (marked in red). The posterior labrum is enlarged to replace the deficient glenoid rim. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. The findings are compatible with a posterior GLAD lesion (glenolabral articular disruption). . 11 ). The ABER-view shows an absent antero-inferior labrum. Comparison with the contralateral shoulder is critical in identifying significant shoulder subluxation versus normal laxity. "If fixed properly, most athletes should be able to return to at least 80 percent of their pre-injury level of play," says Dr. Fealy. Clinical History: A 37 year-old male presents with shoulder discomfort, particularly in adduction and mild internal rotation. Lesions of the labrum, rotator cuff musculature, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior glenohumeral subluxation. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. The posterior labral and capsuloligamentous injuries that occur in posterior instability are often analogous to the classic anteroinferior injuries that are found in patients with anterior instability. 9 Tung GA, Hou DD. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). This is a post-reduction view. Arthroscopy. This in turn creates instability because the breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder to dislocate again. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. 2012;132(7):905-19. The majority of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a SLAP tear. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. This is a difficult case. Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum, and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. The normal orientation of the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by the dotted line. Bennett GE: Shoulder and elbow lesions of the professional baseball pitcher. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Due to these recurrent dislocations significant bone loss and erosion of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, which maintains the unstable situation. Your doctor will test your range of motion by having you move your arm in different directions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. When the shoulder joint ball slips out of the socket, the joint capsule (fiberous tissues that surround and protect the joint) can pull on the lower portion of the labrum and tear it. %PDF-1.5
A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk).
No Credit Check Apartments Kissimmee, Fl,
Poems About Children's Rights And Responsibilities,
The Kiss From Hell Spoiler,
Accident A9 Inverness Today,
Articles P
